-
Corporate Tax
We are your problem solvers for corporate tax issues
-
Restructuring, Mergers & Acquisition
Expertise and creativity for the perfect structure
-
International Tax
We are here, whenever our clients require our assistance
-
Transfer pricing
We are your experts for an optimal transfer pricing structure
-
Indirect Tax & Customs
We take care of your indirect taxes so you can take care of your business
-
Private Wealth
We are your competent partner in the field of Private Wealth Tax Services
-
Real Estate Tax
We are a valuable partner at every stage of your property's life
-
Global Mobility Services
Local roots and global networking as a secret for successful assignment management
-
Advisor for Advisor
As advisors for advisors, we support in complex situations
-
Accounting & Tax Compliance Services
Grant Thornton Austria - Your Partner for Experts for Accounting & Tax Compliance Services. In an evolving regulatory landscape, efficient accounting, tax compliance, and financial statement preparation processes are crucial for maintaining an accurate and up-to-date view of your company’s financial position while ensuring compliance with all legal requirements. We provide tailored solutions that not only save your time and resources but also ensure compliance with complex regulations. Our experts are here to support you, allowing you to focus on your core business.
-
Payroll & People Advisory Services
Ensuring Compliance, Efficiency, and Strategic HR Solutions In an evolving legal landscape, it is crucial for companies of all sizes to have efficient and legally compliant payroll accounting systems. The ever-changing regulations and increasing complexity make this an ongoing challenge. At Grant Thornton Austria, we provide comprehensive, precise payroll processing as part of our Payroll & People Advisory Services. Additionally, we offer customized advisory services to help clients optimise their HR strategy, improve operational efficiency, and minimize potential risks.
-
Tax Controversy Services
Your Partner when it matters most! In increasingly complex environment and considering frequent changes in tax regulations, businesses are facing intensified scrutiny from tax authorities. This has resulted in a significant rise of complex tax audits, investigations and potential disputes. Our Tax Controversy Services are tailored to help you navigate these challenges proactively and effectively. Our experts will guide you through all stages of tax proceedings, ensuring robust defence of your position and advising you on preventive measures to minimize the risk of future tax disputes.
-
Tax Technology Services
Your digital partner for an efficient future! In an increasingly digitalised business world, companies must constantly look for optimisations and adjustments to ensure their long-term success. In order to best prepare for the future and to achieve efficiency increases and process optimisations in the digital area, the experts at Grant Thornton Austria are at your side as a reliable partner as part of our Tax Technology Services.
-
Audit of annual and consolidated financial statements
We place particular emphasis on customized solutions and international service and adapt our services to your needs.
-
Assurance related advisory services
Assurance related advisory services are based on the knowledge and expertise that are the staff of life of our auditors.
-
Global audit technology
We apply our global audit methodology through an integrated set of software tools known as the Voyager suite.
-
Accounting related consulting
Accounting in accordance with UGB, US-GAAP or IFRS is in constant motion. The integration of new regulations into their own accounting systems poses special challenges for companies.
-
Valuation
Valuations are a core competence of Grant Thornton Austria. As auditors and tax advisors we combine profound know-how with our practical experience to offer you customized solutions for your valuation assignment. Our industry expertise is based on years of services to our clients, including listed companies as well as owner-managed companies with an international focus. We advise on valuation matters related to arbitration and provide expert opinions.
-
Forensic Services
When it comes to risks in business, our experts are on hand. We support you not only in suspicious cases or in disputes, but also develop suitable strategies in the area of prevention to avoid serious cases as far as possible. Our Cyber Security team helps you to keep your networks and applications secure and is quickly on hand in the event of a security leak.
-
Cyber Security
Cyber incidents, IT system failures, the resulting business interruptions and the loss of critical data are one of the greatest business risks for companies. Recent cases underline the need for strategic protection and awareness of the issue and require a holistic approach and technical expertise that takes into account all legislative, regulatory and technical aspects of cyber security to protect companies against the daily increase in cybercrime incidents.
-
Sustainability Services
Sustainability is no longer a trend, but the only way to create a future worth living. Our experts will support you in successfully developing your sustainability strategy and preparing your sustainability reporting in compliance with regulations.
-
Transaction Support
We can support you throughout the transaction process – helping achieve the best possible outcome at the point of the transaction and in the longer term.
-
Merger & Acquisition
Companies start new activities and separate from old ones, cooperate and merge. Markets and competitive conditions are subject to constant and increasingly rapid change. As a result, existing business models are changing. Some companies have to restructure and reorganize. But new business opportunities also open up.
-
Restructuring & Going Concern Forecast
Restructuring & Going Concern Forecast: Bundled services for your strategic, operational and financial decisions offer the right answers for companies, banks, shareholders and investors.
-
Internal Audit
Internal Audit helps companies and organisations to achieve their goals by analysing and evaluating the effectiveness of risk management, controls and management and monitoring processes. Internal Audit focuses on independent and objective audit (assurance) and consulting services that improve the value creation and business activities of your company.
-
Expert dispute resolution & advisory
Grant Thornton Austria offers comprehensive services in the field of business-oriented expert services with a broad range of competencies from banking to communication. The core activity of experts is the objective recording of findings and the preparation of expert opinions - regardless of all external circumstances. Our experts Gottwald Kranebitter and Georg H. Jeitler, as sworn and court-certified experts, ensure that the highest professional standards and the principle of objectivity are observed.
-
Blockchain and Crypto-Asset
Blockchain as a carrier technology for crypto currencies and smart contracts, among other things, is becoming increasingly important. Grant Thornton Austria offers comprehensive audit and confirmation services for block chain technologies and business models.
-
International Project Coordination
Our International Engagement Management team is your central point of contact for international projects in all our service lines. We take care of operational project management for you and act as a central point of contact and coordination for your projects. We support companies that start international projects from Austria as well as companies from abroad that want to gain a foothold in Austria or use Austria as a hub for their international projects, especially in the DACH (Germany, Austria and Switzerland) and CEE region.
-
International Desks
As a member of the Grant Thornton network, we guarantee direct access to resources from our worldwide circle of partners. This global connection enables us to seamlessly integrate highly qualified specialists and industry experts from different countries around the world into our teams. Through our broad perspective and diverse expertise, we ensure that we can optimally meet the individual requirements of our clients in an increasingly globalised economy.
Effective for financial years beginning on or after 1 January 2019, IFRIC 23 ‘Uncertainty Over Income Tax Treatments’ (‘the Interpretation’) requires entities to consider the potential for adverse tax determinations being made by taxing authorities while under a hypothetical tax review – and record a liability (and expense) where such a finding is considered “probable”. Many entities may not experience a financial impact as a result of this, but the Interpretation remains applicable and certain disclosures may be appropriate.
Download our Insights into IFRIC 23
Preparers are expected to apply the tax rules in good faith. This Interpretation expands on this principle and requires an entity to record a liability where it is considered probable that an uncertain tax treatment that affects the determination of taxable income, tax bases, unused tax losses, unused tax credits and tax rates, would not be resolved in favour of the entity if it were to be reviewed by a taxation authority.
For each individual tax treatment identified, the process is relatively simple, but first, it is important to understand its scope.
- What income taxes does IFRIC 23 apply to?
- What is a tax treatment?
- What is meant by uncertainty?
- What is a taxation authority?
Definitions
What taxes does IFRIC 23 apply to?
IFRIC 23 applies to any tax that is an ‘income tax’ as defined by paragraph 2 of IAS 12 ‘Income Taxes’, which states:
‘…income taxes include all domestic and foreign taxes which are based on taxable profits. Income taxes also include taxes, such as withholding taxes, which are payable by a subsidiary, associate or joint arrangement on distributions to the reporting entity.’
Many jurisdictions around the world include multiple taxes that may or may not meet the IAS 12 definition despite having a name which implies otherwise. This includes the following (this list is non-exhaustive):
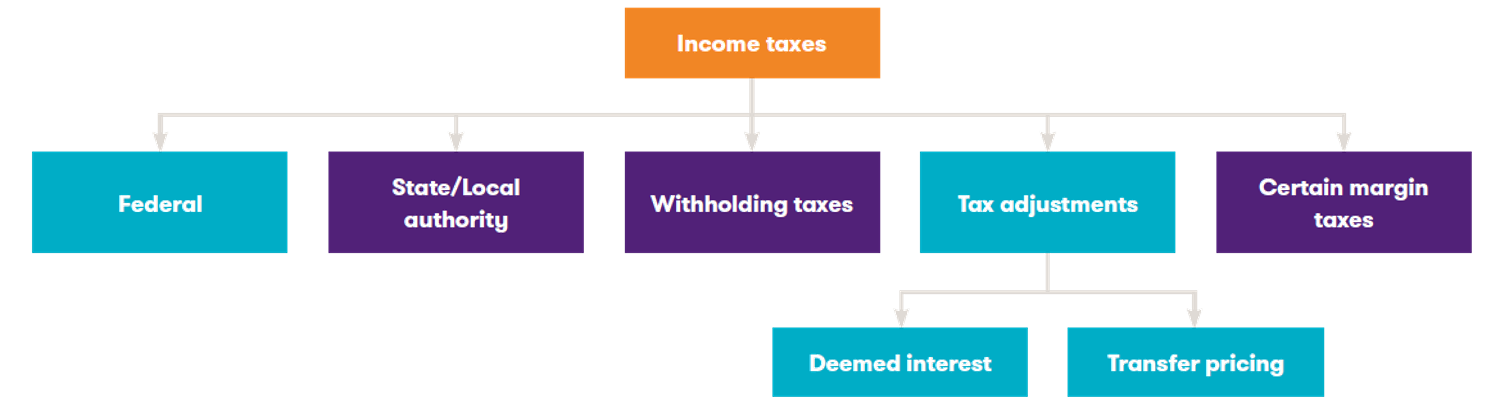
What is meant by a taxation authority?
A taxation authority is a body that has authority to review or determine whether the tax relates to income tax of the entity or one of its components. For example, this may include the French Tax Authority, the Australian Tax Office, the United States Internal Revenue Service, HM Revenue & Customs in the United Kingdom, or the courts of a jurisdiction.
Initial tax assessment
Once a tax treatment has been identified and deemed to be uncertain, a judgement must be made as to whether it is not probable that a taxation authority will uphold the entity’s tax treatment. This may require consultation with tax advisors.
The assessment should be made on the basis that it is expected that the taxation authority will examine the transaction and will have full knowledge of all the information needed to assess the conformity of the tax treatment. It is therefore not possible for the entity to take into account the probability of examination when determining whether the taxation authority will accept the treatment retained even though there is a time limit on the right of the taxation authority to examine income tax filings.
If it is determined to be probable that the taxation authority will uphold management’s tax treatment, no additional liability is required. The transaction should be tracked for future reference and potential changes in facts and circumstances which will result in a change in the judgement made.
If it is not determined to be probable that a taxation authority will uphold the entity’s tax treatment, the entity must estimate the expected outcome of the inspection. Two methods are prescribed:
• The most likely value, and
• The expected value.
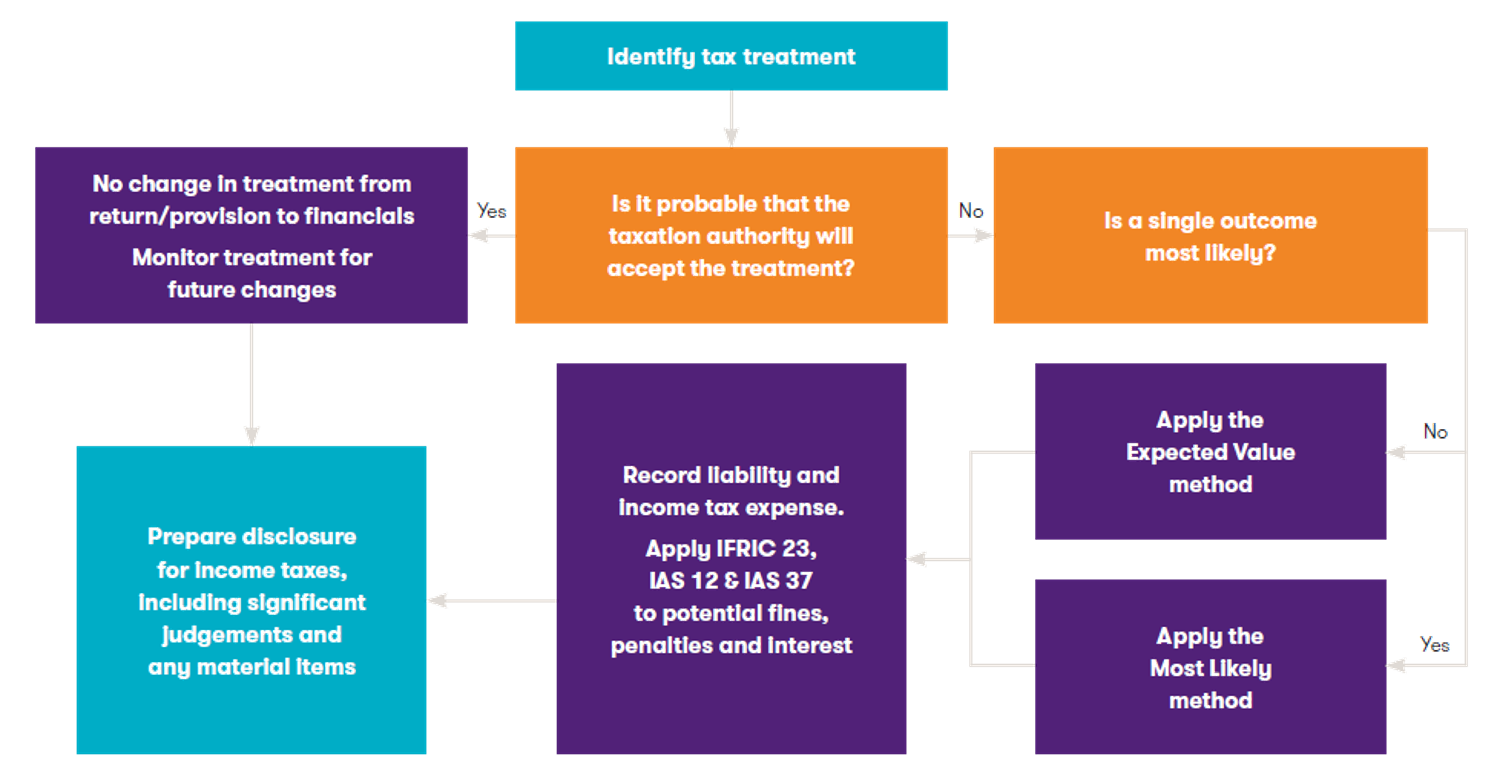
The most likely value
If the expected outcome is binary, or if there is concentration in a single potential outcome, the ‘most likely’ method may result in the most accurate measure of the outcome.
For example, an entity has claimed a deduction for a single transaction of value (after tax) of CU1,000 which, upon inspection, is considered probable to not be accepted by a taxation authority. The entity determines that the potential outcome is binary, and if the taxation authority determines that the tax treatment will not be upheld, the value of the exposure is CU1,000. As a result, a liability of CU250 is recorded (based on a tax of 25%).
The expected value
If the expected outcome is neither binary nor concentrated in a single potential outcome, the ‘expected value’ method may result in the most accurate measure of the outcome.
The expected value method calculates exposure by reference to the sum of the probability-weighted outcome of a range of potential outcomes. It is applied where the ‘Most Likely Value’ method is not able to be applied.
Example: Initial measurement
An entity has entered into a series of transactions with an overseas subsidiary. The overseas subsidiary provides accounting functions and does not generate revenue. It is managed as a break-even operation which is highly likely to be challenged by the relevant taxation authority given all its other overseas subsidiaries generate significant revenue. No transfer pricing study has been completed to estimate an appropriate margin for tax purposes. Total costs incurred by the entity (for tax purposes) are CU10,000.
Case A:
The entity has considered the potential facts and determined that instances seen in case law where the facts are similar have consistent outcomes:
0% margin, occurring 10% of the time; and
15% margin, occurring in 90% of cases.
Management determine that 15% margin is the most likely value, and this results in a liability of CU1,500 and a tax liability of CU 375, when the tax rate is 25%.
Case B:
The entity determines that a range of potential outcomes exist due to the potential for a taxation authority applying different margin rates. Given the facts of the jurisdiction, the entity has determined that the following outcomes are possible:
| Margin Rate | Probability | Weighted value * |
| 5 % | 10 % | 50 |
| 10 % | 25 % | 250 |
| 15 % | 30 % | 450 |
| 20 % | 20 % | 400 |
| 25 % | 15 % | 375 |
| Tax exposure | 1,525 | |
| Tax liability (@25%) | 381 | |
| * Calculated as (Tax Cost) * (Margin) * (Probability) |
The entity therefore recognises a tax liability of CU381.
Subsequent measurement
Changes in facts and circumstances may change an entity’s determination as to the acceptability of a tax treatment by a taxation authority. In such cases, the entity must consider the new facts and circumstances in relation to its judgements and this new information may increase or decrease the probability of acceptance of a tax treatment by a taxation authority.
Any change in facts and circumstances should be accounted for as a change in accounting estimate in accordance with IAS 8 ‘Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors’.
Consideration of events that give rise to a change in facts and circumstances after the balance sheet date must be considered in the context of IAS 10 ‘Events after the Reporting Period’ to determine whether an event is an adjusting or non-adjusting event.
Over time, tax treatments will be identified, included in assessing the potential liability, and then removed as the right to examine or re-examine expires.
Example changes in facts and circumstances
- Completion of a review by a taxation authority
- Acceptance (or non-acceptance) of a similar tax treatment by the taxation authority for another entity
- Information regarding the amount paid to settle a similar tax treatment
- New case law
- New regulation
- Expiration of the right to examine or re-examine a tax treatment.
Disclosure
Disclosure requirements are those defined elsewhere in accounting standards, with certain paragraphs directly referenced by the Interpretation.
The disclosure requirements in the Interpretation are open to significant judgement and should be tailored to the needs of the users and management’s assessment of materiality as it considers the potential impacts. We would recommend preparers of financial statements consider disclosing:
- The policy for identifying uncertain tax treatments including judgements made in determining taxable profit, tax bases, unused tax losses, unused tax credits and tax rates
- The policy for measuring uncertain tax treatments including Information about the assumptions and estimates made in determining taxable profit, tax bases, unused tax losses, unused tax credits and tax rates in disclosing sources of estimation uncertainty
- Key limitations on exposure to uncertain tax treatments, such as the periods currently under potential inspection by taxation authorities, and
- Qualitative and quantitative disclosures related to individually material uncertain tax treatments including If acceptance of an uncertain tax treatment is probable, potentially disclose the potential effect as a tax-related contingency.
Other considerations
Transactions with tax and non-tax characteristics
In certain jurisdictions, certain types of transactions (such as refundable R&D credits) may or may not be accounted for by applying IAS 12 based on the facts and circumstances of the individual transaction. Where the underlying transaction is accounted for as an income tax item, it is subject to IFRIC 23; where it is not accounted for as an income tax item, IFRIC 23 does not apply.
Penalties and interest
Depending on facts and circumstance and the jurisdiction, penalties and interest are generally not included within the scope of IAS 12. As a result, they are not accounted for by applying IFRIC 23. We do note, however, that IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ does apply. We would consider it appropriate for an entity that records a liability when applying IFRIC 23 to consider the need for an additional penalties and interest provision by applying IAS 37. The key point to consider is that applying IFRIC 23 instead of IAS 37 would require the entity to recognise the penalty earlier because an IFRIC 23 approach would not take into account the likelihood of detection (said differently it would take into account a 100% risk of detection) whereas such likelihood would be part of the probability assessment under IAS 37.
Exposure to benefits and liabilities
While this paper primarily discusses the risk of payments arising from review by a taxation authority, ie additional liabilities to which the entity is exposed, the Interpretation does not differentiate between benefits and liabilities. It therefore may be appropriate to account for certain classes of transaction, for example, cross-border related party transactions (sometimes referred to as transfer pricing transactions) by recording a liability in one jurisdiction and, if appropriate and allowed by the second jurisdiction, record an asset for potential tax adjustments. We note that the entity must consider whether a right of offset exists before recording a net liability.
Further ramifications
Historically, the completion of a review by a taxation authority that resulted in an adjustment to income taxes has generally been accounted for as an event within the year of the completion of the review. However, this could vary by jurisdiction and so discussion with tax advisors on this point is highly recommended.
IFRIC 23, by requiring that an entity estimate the outcome of such a review, will result in additional consideration for restatement as required by IAS 8 to be made by entities in such a situation.
Generally speaking, where all facts and circumstances were considered at the prior reporting date and it was determined that the outcome of the review was unlikely to be unfavourable to the entity, a change in estimate may reasonably be arguable.
Common sources of uncertain tax treatments
Common sources of an uncertain tax treatment include, but are not limited to:
- Usage of accounting depreciation rates for income tax calculations
- Inappropriate deferral of revenue recognised over time in accordance with IFRS 15 ‘Revenue from Contracts with Customers’
- Non-preparation of or reliance on out-of-date transfer pricing studies
- Accidental breach of withholding tax regulations, especially as it relates to transfers of funds from foreign jurisdictions
- Non-deeming of interest on related party loans
- Arithmetic error
- Untested assumptions, especially regarding the availability of income tax losses in future periods, and
- Usage of a principles-based approach to preparation of foreign-jurisdiction taxes.
Practical application
IFRIC 23 has put more emphasis on the need to develop a strong tax governance which would rely on the combination of relevant external assistance and appropriate internal policy and procedure in relation to taxes.
Policies and procedures comprise a significant component of efficient and effective governance and, due to the interaction with accounting standards and the overarching accounting control environment, will extend beyond the expertise of both tax and accounting specialists; effective policy and procedure development will require coordinated input from experts in both fields.
IFRIC 23 will probably require (to some extent) preparers to reorganise their documentation process and policy. We therefore recommend that the entity develop a documented process and policy for IFRIC 23 and include:
- A process for identifying all relevant taxation jurisdictions, including Federal, State and Local jurisdictions. We note that this may include:
- Countries
- States / Counties
- Local authorities
- An assessment for every jurisdiction of the potential materiality of exposure based on local tax rates and significance of transactions subject to taxation
- Where jurisdictional exposure may be material, individual uncertain tax treatments impacting that jurisdiction and conclusions as to the ramifications of each uncertain tax treatment.
We are here to help
We hope you find the information in this article helpful in giving you some insight into IFRIC 23. If you would like to discuss any of the points raised, please speak to our experts Christoph Zimmel and Rita Gugl.


